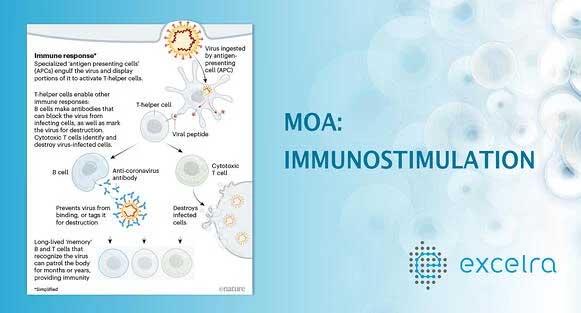
Although three human coronaviruses namely: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 have hit mankind in last two decades, no vaccines have yet been developed against them. Vaccines are the most effective strategy for preventing infectious disease including viral diseases like COVID-19. Specialized antigen presenting cells ingest the virus and present the viral antigens to activate the Helper T-cells.
These Helper T-cells can function in the following two ways:
1. Activate B-cells to produce large quantity of anti-viral antibodies
2. Activate Cytotoxic T-cells to identify and clear the virus infected cells.
In this process, long-lived memory B-cells and T-cells are generated in the body to develop long term immunity against the virus. Among the two mechanisms being activated, T-cell mediated immunity is the most important mechanism to tackle the viral infections.
In the current global scenario, a range of technologies are being used to develop the COVID-19 vaccine. Some of the approaches include: nucleic acid (DNA and RNA), virus-like particle, peptide, viral vector (replicating and non-replicating), recombinant protein, live attenuated virus and inactivated virus approaches. A US vaccine company, Moderna started clinical testing of its mRNA-based vaccine mRNA-1273 within two months of sequence identification. Some of the vaccine candidates in Phase-I testing are: mRNA-1273 (Moderna), Ad5-nCoV (CanSino Biologicals), INO-4800 (Inovio Pharmaceuticals), LV-SMENP-DC (Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute) etc.
Whatever may be the approach adopted for the vaccine development, it must be safe and develop long term immunity against the SARS-CoV-2.
Excelra’s open-access COVID-19 Drug Repurposing Database is a synoptic compilation of ‘Approved’ small molecules and biologics, which can rapidly enter either Phase 2 or 3, or may even be used directly in clinical settings against COVID-19. The database additionally includes information on promising drug candidates that are in various clinical, pre-clinical and experimental stages of drug discovery and development.
Supported with referenced literature, we provide mechanistic insights into SARS-CoV-2 biology and disease pathogenesis. We hope that these drug repositioning approaches can help the global biotech and pharma community develop treatments to combat COVID-19.


